We use this tense when we refer to:



Past Simple of the verb be
We use the simple past to talk about a past situation.

Past Simple of Regular and Irregular verbs
We use the simple past to talk about actions or situations that happened and finished in the past, a completed action. We usually say or know when the action happened.


Time expressions

- This week/month/year
- Every day
- Every week/month/year
- Often
- Never
- Once/twice a day
- On Mondays/Tuesdays...
- Yesterday
- Last week/month/year
- This morning
- A week ago
- Long time ago
- Recently
- In 1997
- When I was born
Continuous Form
The continuous or progressive tense is formed with the verb "be" + - ing form of the verb.
We use this form to talk about present or past actions in progress.

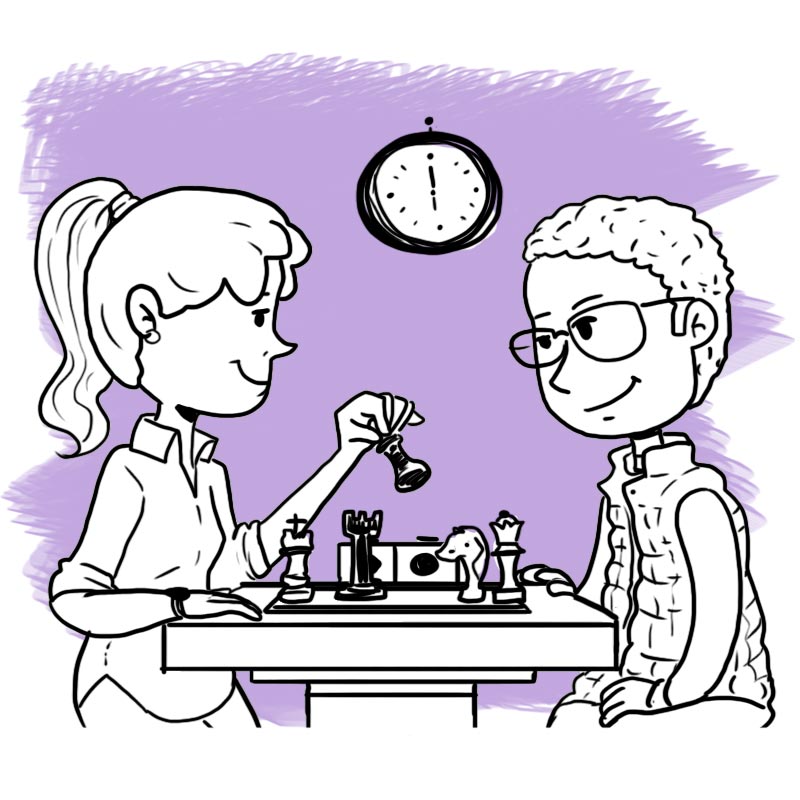
Alexei and Romina are excellent chess players, they are participating in the World Chess Championship.
Yesterday Alexei and Romina played chess. They began at 11 a.m. and finished at 11 p.m.
What were they doing yesterday at 6 p.m.?
They were playing chess.
Today, the competition continues, it’s 11 a.m. What are Romina and Alexei doing?
They are playing chess.
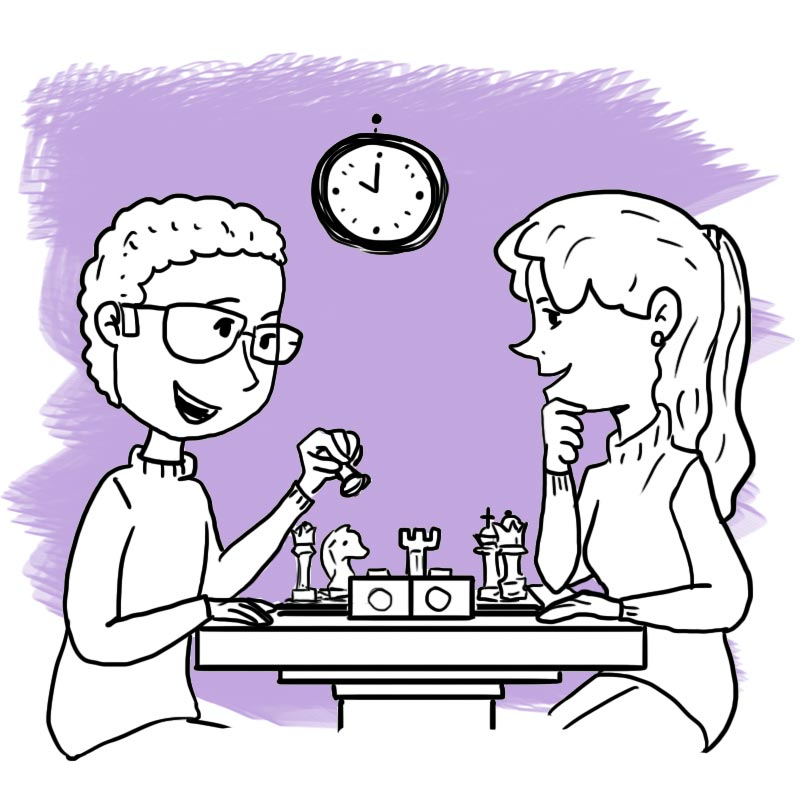



Past Continuous
We often use the past continuous (I was doing) and the past simple (I did) in the same sentence. The action in the past simple is short, and usually unexpected. It interrupts the longer action in the past continuous.
We sometimes use words as WHEN and WHILE when we want to connect two actions:
Use While to refer to two continuous actions at the same time.
Use When to refer to two actions that happened at the same time, one action (usually short action) interrupts the action in progress.

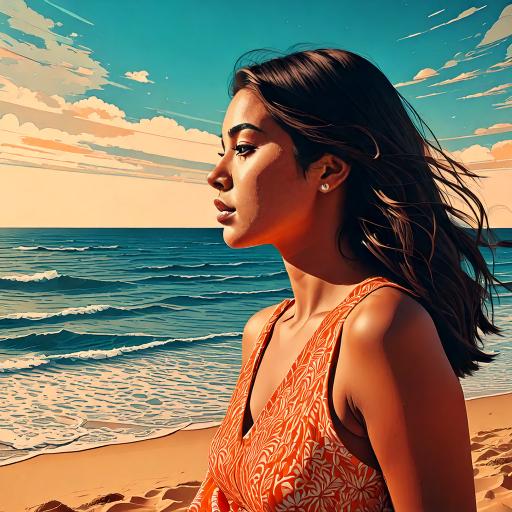
Last summer Sophie went to the beach, one day she...
| Sophie was relaxing on the beach | she saw two dolphins playing in the water. | she was recording them, the dolphins were flipping. | She posted her story on Instagram and she got hundreds of "likes". | |||
 |
when |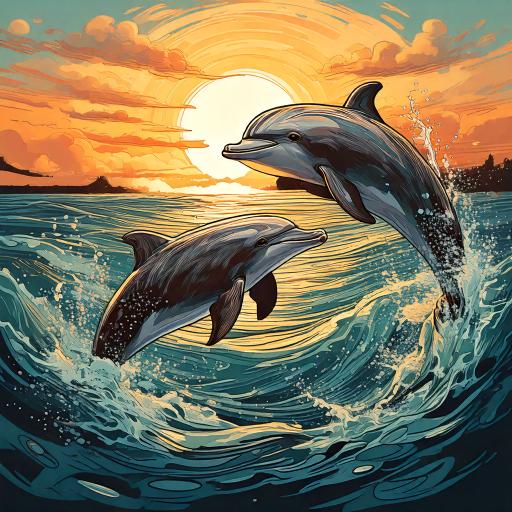  |
While |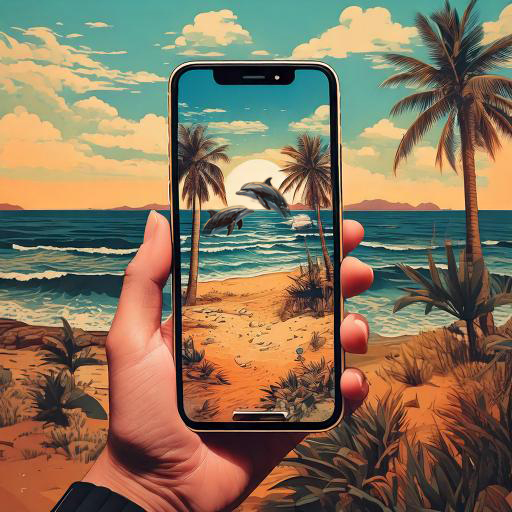  |
Later, |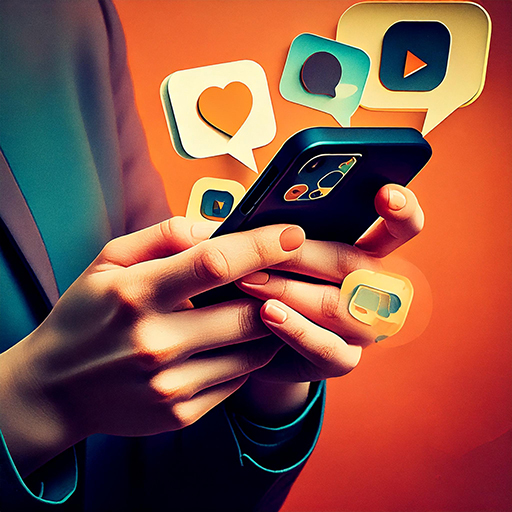  |
Linking words
Linking words are words that join two or more words, sentences or clauses. Linking words are also called conjunctions. We can use them to express different ideas.

| Use | Word | Example |
| To show CONTRAST | However, it is used to connect two ideas in two separate sentences. We put 'however' in the second sentence and a comma after it. | It was raining very hard. However, we went out and enjoyed ourselves. |
| Although use 'although' at the beginning or in the middle of a sentence. Use a comma after the first sentence. | Although it was raining very hard, we went out and enjoyed ourselves. We went out and enjoyed ourselves, although it was raining very hard. |
|
| But Use "but" to connect ideas that contrast. Use it at the beginning of the second sentence after a comma. | It was raining very hard, but we went out and enjoyed ourselves. | |
| To express REASON | Because Use "because" to connect the result of something with its reason. | Thousands of women in Mexico attended the 8M march because they demanded equality. |
| And Use "and" to connect two words, clauses or phrases together. | U.S. women soccer players are fighting for equal pay and benefits. | |
| To ADD information | So Use "so" to introduce clauses of result or decision. | Frida loved life, so her paintings were colorful and intense. |
| Or Use "or" to connect possibilities or choices. | We can do nothing to protect the environment or we can start reducing, reusing, and recycling. |
Sequencers
Sequencers are words that we use when we talk about the order of doing things. We use these words when we give instructions, or describe the order in which an event happened. You can use these words to sequence events and to make stories and anecdotes more interesting.
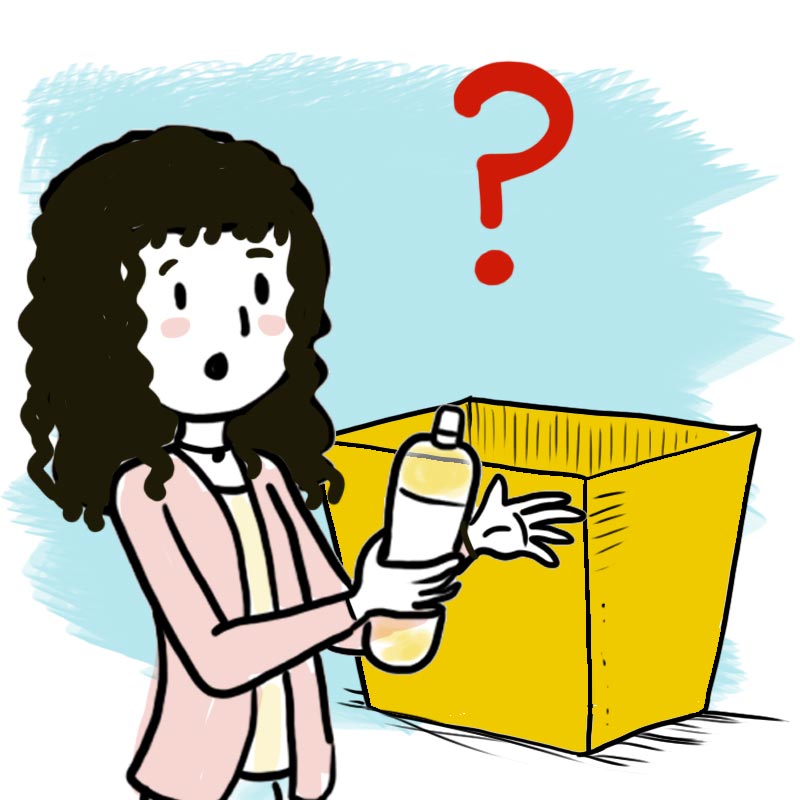

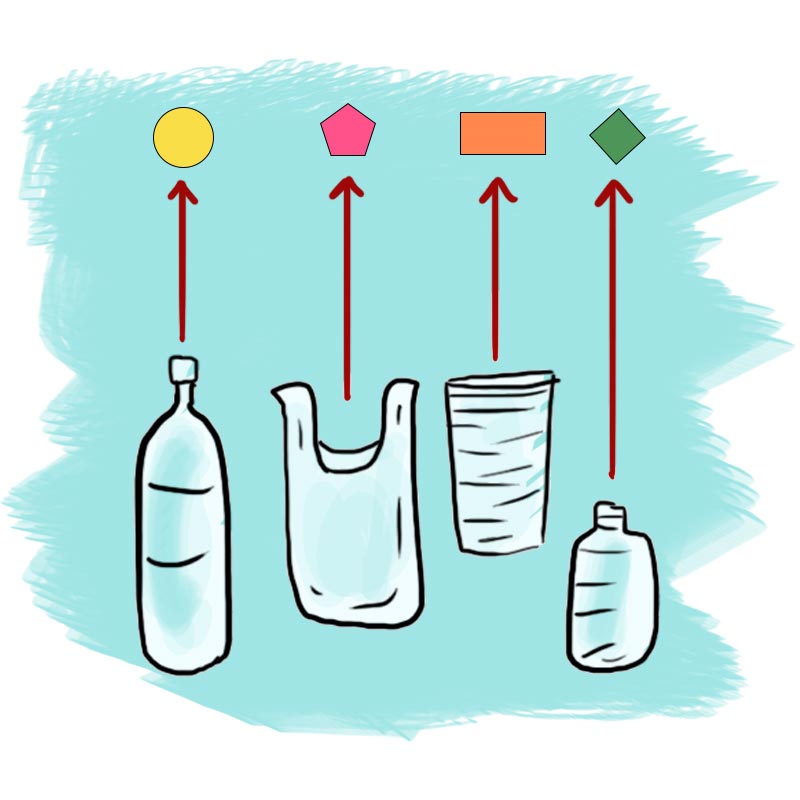
What will happen to this water bottle after I’m finished with it?
Let’s see, plastic recycling involves the following steps.
Read the descriptions and tick the corresponding tense.
| Present simple | Present continuous | Past simple | Past continuous | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| We use this tense to talk about actions that happened simultaneously in the past. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to talk about habitual or repeated actions. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to talk about actions taking place for a limited time. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to refer to actions that are generally true. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to talk about actions happening at the moment of speaking. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to talk about actions that happened in the middle of another action. |
|
|
|
|
| We use this tense to talk about actions completed in the past. |
|
|
|
|
Look at these time expressions, put them in the correct column.
Present
Past
Read the sentences describing how to download an image from the internet. Select the option that presents the correct order of the steps.
click download.
type what you want to search.
open your browser.
save it in your folder.
click on the image.